
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
Install NowCBSE will ask Case Study Questions class 12 Chemistry in session 2020-21. These will be the first two questions in the board exam question paper. The first question will have 5 MCQs out of which students will attempt any 4 questions. The second question will carry 5 Assertion & Reason type questions with the choice to attempt any four.

Case Study Questions
As you know, CBSE will hold exams in May-June this year. There is already a reduction of 30% in the syllabus. Now, the case study questions have been added. So, this year the question paper is going to be a bit easier. Although it is easy yet these case study questions need special attention and regular practice.
We have added around 10 sample questions based on the latest pattern in myCBSEguide App. These all questions include two case study questions.
Class 12 Chemistry Question Bank
If you go through the previous year question papers, you will analyze that many questions are repeated word by word and many others are almost similar. So, it is always recommended to check all questions asked in previous years. This will not only help you to get an idea about the question pattern but also help you to understand the difficulty level of the questions.
myCBSEguide App has the previous year’s question bank. These questions are arranged chapter-wise. If you are preparing a particular chapter, you will get all questions asked from that chapter in the last 10 years.
Case Study Questions Examples
Here are two examples of case study questions. To get more such questions download the myCBSEguide App and browse Sample Papers there.
Read the passage given below and answer any four out of the following questions:
Ammonia is present in small quantities in air and soil where it is formed by the decay of nitrogenous organic matter e.g., urea. On a large scale, ammonia is manufactured by Haber’s process. In accordance with Le Chatelier’s principle, high pressure would favour the formation of ammonia. Ammonia is a colourless gas with a pungent odour. Its freezing and boiling points are 198.4 and 239.7 K respectively. In the solid and liquid states, it is associated through hydrogen bonds as in the case of water and that accounts for its higher melting and boiling points than expected on the basis of its molecular mass. Ammonia gas is highly soluble in water. Its aqueous solution is weakly basic due to the formation of OH– ions. The presence of a lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom of the ammonia molecule makes it a Lewis base.
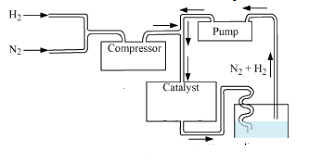
The following questions are multiple-choice questions. Choose the most appropriate choice
- On a small scale, ammonia is obtained from ammonium salts which decompose when treated with
- caustic soda
- calcium chloride
- sodium hydroxide
- sodium chloride
- The optimum conditions for the production of ammonia are a pressure of
- 200 105 Pa
- 400 105 Pa
- 100 105 Pa
- 300 105 Pa
- The catalyst which is used in the preparation of NH3 by Haber’s process
- Mg2O3 + K2O
- Al2O3 + K2O
- NaO3 + K2O
- None of these
- The ammonium molecule has:
- five bond pair and two lone pair
- four lone pair and one bond pair
- three bond pair and one lone pair
- three bond pair and two lone pair
- A compound reacts with ammonia to form deep colour solution, identify the compound
- Au2+
- Cu2+
- Al3+
- Mg2+
Read the passage and answer any four out of the following questions:
Colloidal particles always carry an electric charge. The nature of this charge is the same on all the particles in a given colloidal solution and may be either positive or negative. The charge on the sol particles is due to one or more reasons, viz., due to electron capture by sol particles during electrodispersion of metals. When two or more ions are present in the dispersion medium, preferential adsorption of the ion common to the colloidal particle usually takes place. When silver nitrate solution is added to the potassium iodide solution, the precipitated silver iodide adsorbs iodide ions from the dispersion medium, and negatively charged colloidal solution results. acquired a positive or a negative charge by selective adsorption on the surface of a colloidal particle The combination of the two layers of opposite charges around the colloidal particle is called Helmholtz electrical double layer. The presence of equal and similar charges on colloidal particles is largely responsible for providing stability to the colloidal solution.
In these questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
- Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion
- Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion
- Assertion is correct statement and reason is wrong statement
- Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement
- Assertion: The presence of equal and similar charges on colloidal particles is largely responsible in providing stability to the colloidal solution.
Reason: The repulsive forces between charged particles having the same charge prevent them from aggregating and provide stability. - Assertion: The first layer is mobile in Helmholtz electrical double layer.
Reason: The potential difference between the fixed layer and the diffused layer of opposite charges is called zeta potential. - Assertion: The sol particle in colloid has a charge.
Reason: The charge in sol is due to electron capture by sol particles during the electrodispersion of metals. - Assertion: Methylene blue sol is a negatively charged sol.
Reason: When KI solution is added to AgNO3 solution, positively charged sol formed. - Assertion: If FeCl3 is added to an excess of hot water, a positively charged sol of hydrated ferric oxide is formed.
Reason: When ferric chloride is added to NaOH a negatively charged sol is obtained with adsorption of OH- ions.

Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Create Now
myCBSEguide
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Install Now
Answer for questions