
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
Install NowCBSE will ask two Case Study Questions in the CBSE class 12 Physics questions paper. Question numbers 15 and 16 are case-based questions where 5 MCQs will be asked based on a paragraph. Each theme will have five questions and students will have a choice to attempt any four of them. You can download CBSE Class 12 Physics case study questions from the myCBSEguide App and our free student dashboard.

You can Score High
CBSE class 12 Physics question paper will carry questions for 70 marks. Certainly, the question paper is a bit easier this year. It is because the syllabus is already reduced and there are more internal choices. Besides this, the case study questions are a plus to winning the game with good marks.
In simple words, all circumstances are in favour of the sincere students who are working hard to score high this year. Although it has been a difficult time for students as they were not getting the personal attention of the teachers. We know that online classes have their own limits, but we still expect better scores, especially from students who are putting extra effort into their studies.
Class 12 Physics Case Study Questions
CBSE class 12 Physics question paper will have case study questions too. These case-based questions will be objective type in nature. So, class 12 Physics students must prepare themselves for such questions. First of all, you should study NCERT Textbooks line by line and then you should practice as many questions as possible.
Case Study Syllabus
We know that CBSE has reduced the syllabus. Hence, practice only relevant questions. don’t waste time on case study questions from deleted portion. It is of no use. You can download the latest class 12 Physics case study questions from the myCBSEguide App.
Physics Case Studies
Class 12 Physics has many chapters but all chapters are not important for case studies. As we know case studies are not exactly given from NCERT books but these may be extracted from some newspaper articles, magazines, journals or other books. So, it is very much important that you are studying only the most relevant case studies. Here, the myCBSEguide app helps you a lot. We have case study questions that are prepared by a team of expert teachers. These experts exactly know what types of questions can come in exams.
Case Study Questions
There are a number of study apps available over the internet. But if you are a CBSE student and willing to get an app for the CBSE curriculum, you have very limited options. And if you want an app that is specifically designed for CBSE students, your search will definitely end on finding myCBSEguide. Case study questions are the latest updates in CBSE syllabus. It is exclusively available in the myCBSEguide app.
12 Physics Case Study Questions
Here are some example questions. For more questions, you can download the myCBSEguide App.
Physics Case Study -1
Read the following source and answer any four out of the following questions:
Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. There are two types of charges positive and negative charges. Also, like charges repel each other whereas unlike charges attract each other.
- Charge on a body that carries 200 excess electrons is:
- -3.2 ×× 10-18 C
- 3.2 ×× 10 18 C
- -3.2 ×× 10-17 C
- 3.2 ×× 10 -17 C
- Charge on a body that carries 10 excess electrons is:
- -1.6 ×× 10-18 C
- 1.6 ×× 10 -18 C
- 2.6 ×× 10-18 C
- 1.6 ×× 10-21 C
- Mass of electron is:
- 9.1 ×× 10-31 kg
- 9.1 ×× 10-31 g
- 1.6 ×× 10-19 kg
- 1.6 ×× 10-19 g
- A body is positively charged, it implies that:
- there is only a positive charge in the body
- there is positive as well as negative charge in the body but the positive charge is more than the negative charge
- there is equally positive and negative charge in the body but the positive charge lies in the outer regions
- the negative charge is displaced from its position
- On rubbing, when one body gets positively charged and the other negatively charged, the electrons transferred from the positively charged body to the negatively charged body are:
- valence electrons only
- electrons of inner shells
- both valence electrons and electrons of the inner shell.
- none of the above
Physics Case Study -2
Read the following source and answer any four out of the following questions:
Resistance is a measure of the opposition to current flow in an electrical circuit. Resistance is measured in ohms. Also, Resistivity is the electrical resistance of a conductor of unit cross-sectional area, and unit length. … A characteristic property of each material, resistivity is useful in comparing various materials on the basis of their ability to conduct electric currents.
- Resistivity is independent of:
- nature of material
- temperature
- dimensions of material
- none of the above
- As compared to short wires, long wires have _______ resistance.
- more
- less
- same
- zero
- As compared to thin wires, thick wires have _______ resistance.
- more
- less
- same
- zero
- The resistance of a wire depends upon:
- cross-sectional area
- length of wire
- wire’s nature
- all of the above
- A copper wire having the same size as steel wire have:
- more resistance
- less resistance
- same resistance
- none of the above
Physics Case Study -3
Read the source given below and answer any four out of the following questions:
The Bohr model of the atom was proposed by Neil Bohr in 1915. It came into existence with the modification of Rutherford’s model of an atom. Rutherford’s model introduced the nuclear model of an atom, in which he explained that a nucleus (positively charged) is surrounded by negatively charged electrons.
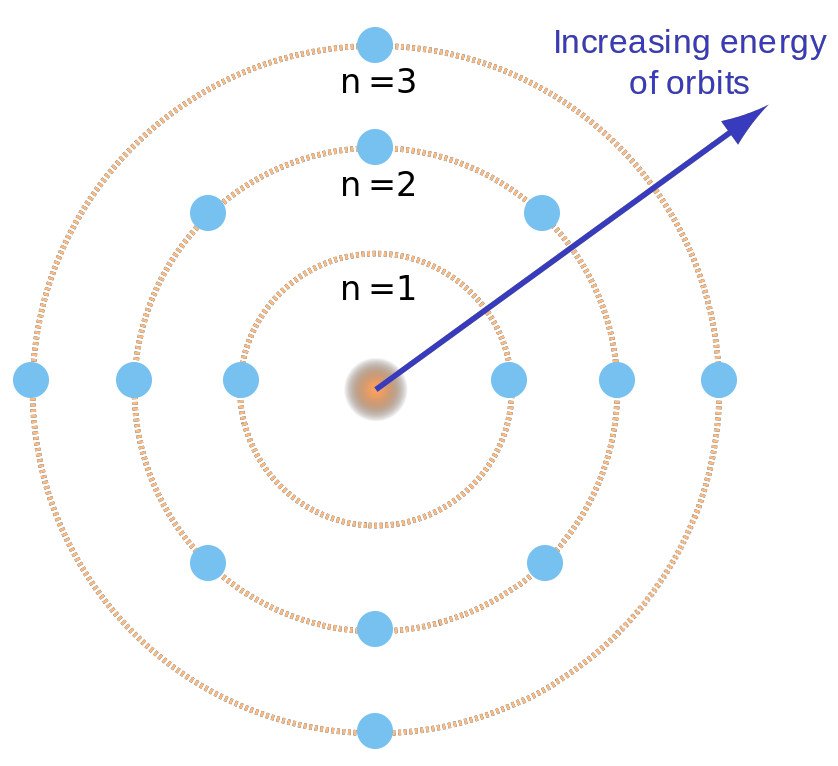
- Which of the following statements does not form a part of Bohr’s model of a hydrogen atom?
- The energy of the electrons in the orbit is quantized
- The electron in the orbit nearest the nucleus has the lowest energy
- Electrons revolve in different orbits around the nucleus
- The position and velocity of the electrons in the orbit cannot be determined simultaneously
- What is in the center of the Rutherford model?
- Single proton
- Multiple electrons
- A nucleus
- Neutrons
- When an electron jumps from its orbit to another orbit, energy is:
- emitted only
- absorbed only
- both (a) and (b)
- none of these
- What were the limitations of the Rutherford model which could not explain the observed features of atomic spectra explained in Bohr’s model of a hydrogen atom?
- It must emit a continuous spectrum
- It loses its energy
- Gaining its energy
- A discrete spectrum
- When an electron remains between orbits its momentum is:
- quantized
- emitted
- dequantized
- none of the above
Physics Case Study & myCBSEguide App
We at myCBSEguide provide the best case study questions for CBSE class 12 Physics. We have Physics case study questions for every chapter in 12th class Physics. Students can access the Physics case study questions with answers on the myCBSEguide App or on the student dashboard. Here are some features that make myCBSEguide the best learning app for CBSE students:
- Updated syllabus
- Up to date question bank
- Model papers and 10-year questions
- NCERT and Exemplar sulutions
- Best quality learning videos
- Detailed revision notes
12 Physics Question Paper Design
Here is the question paper design for CBSE class 12 Physics. It shows the typology of the questions and their weightage in CBSE board exams.
QUESTION PAPER DESIGN
Theory (Class: 12)
Maximum Marks: 70
Duration: 3 hrs
| S | Typology of Questions | Total Marks | Approximate Percentage |
| Remembering: Exhibit memory of previously learned material by recalling facts, terms, basic concepts, and answers. Understanding: Demonstrate understanding of facts and ideas by organizing, comparing, translating, interpreting, giving descriptions, and stating main ideas | 27 | 38% | |
| Applying: Solve problems to new situations by applying acquired knowledge, facts, techniques and rules in a different way | 22 | 32% | |
| Analysing: Examine and break information into parts by identifying motives or causes. Make inferences and find evidence to support generalizations Evaluating: Present and defend opinions by making judgments about information, the validity of ideas, or quality of work based on a set of criteria. Creating: Compile information together in a different way by combining elements in a new pattern or proposing alternative solutions. | 21 | 30% | |
| Total Marks | 70 | 100 | |
| Practical | 30 | ||
| Gross Total | 100 |
Note: The above template is only a sample. Suitable internal variations may be made for generating similar templates keeping the overall weightage to different forms of questions and typology of questions the same.

Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Create Now
myCBSEguide
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Install Now
Good question l will check answers sheet
Question 2 answer key ?