
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
Install NowCBSE class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals notes in PDF are available for free download in myCBSEguide mobile app. The best app for CBSE students now provides Metals and Non-metals class 10 Notes latest chapter wise notes for quick preparation of CBSE board exams and school based annual examinations. Class 10 Science notes on Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals are also available for download in CBSE Guide website.
CBSE Guide Metals and Non-metals class 10 Notes
CBSE guide notes are the comprehensive notes which covers the latest syllabus of CBSE and NCERT. It includes all the topics given in NCERT class 10 Science text book. Users can download CBSE guide quick revision notes from myCBSEguide mobile app and my CBSE guide website.
10 Science notes Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals
Download CBSE class 10th revision notes for Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals in PDF format for free. Download revision notes for Metals and Non-metals class 10 Notes and score high in exams. These are the Metals and Non-metals class 10 Notes prepared by team of expert teachers. The revision notes help you revise the whole chapter in minutes. Revising notes in exam days is on of the best tips recommended by teachers during exam days.
Download Revision Notes as PDF
CBSE CLass 10 Science
Revision Notes
CHAPTER – 3
METALS AND NON-METALS
- About 118 elements are known today. There are more than 90 metals,22 non metals and a few metalloids.
- Sodium (Na), potassium (K), magnesium(Mg), aluminium(Al),calcium(Ca), Iron(Fe), Barium(Ba) are some metals.
- Oxygen(O), hydrogen(H), nitrogen(N), sulphur(S), hosphorus(P),fluorine(F), chlorine(Cl), bromine(Br), iodine(l) are some non-metals.
| Metals | Non-metals | ||
| 1. | Generally solid except Hg(present in liquid form). | 1. | Can be solid, liquid organs e.g., C is solid, Br (liq), H(gas) |
| 2. | Ductile, Malleable (drawn into wires) (beaten into sheets) | 2. | Non-ductile, non-Malleable |
| 3. | Sonorous (produces sound) | 3. | Non-sonorous |
| 4. | Lustrous (have natural shine) | 4. | Non-lustrous except Iodine. |
| 5. | High Melting Point except Ce and Ga | 5. | Lower M.P. than metals. |
| 6. | Generally good conductors of heat and electricity except Pb and Hg. | 6. | Bad conductors of heat and electricity except Graphite (form of C) |
| 7. | High density except Na and K | 7. | Low densities except Diamond (form of C) |
| 8. | Reactive | 8. | Not very reactive. |
| 9. | Ionic bonding is present, | 9. | Covalent/Hydrogen bonding is present |
- Metals form basic oxides e.g., Magnesium oxide(MgO), while non-metals form acidic oxides e.g., .
- Ag and Cu are best conductors of electricity.
- Metals and Non-metals can be distinguished on the basis of their physical and chemical properties.
- Some elements show the properties of both metals and non-metals and are called metalloids.
Chemical Properties of Metals Reaction with air : Different metals show different reactivities towards oxygen present in air. Metal Oxide
- Some metals like Na and K are kept immersed in kerosene oil as they react vigorously with air and catch fire.
- Some metals like Mg, Al, Zn, Pb react slowly with air and form a protective layer.
- Mg can also burning air with a white dazzling light to form its oxide
- Fe and Cu don’t burn in air but combine with oxygen to form oxide.Iron filings burn when sprinkled over flame.
- Metals like silver, platinum and gold don’t burn or react with air.
e.g..
Usually metal oxides are basic in nature,but some metal oxides show both acidic and basic nature. Amphoteric Oxides :metal oxides which react with both acids as well as bases to form salt and water e.g.
eg..
REACTION WITH WATER : Metal oxides on reaction with water form alkalis. 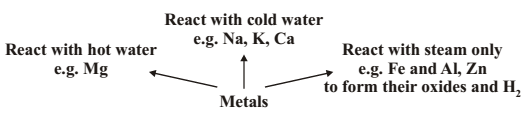
In case of Ca and Mg, the metal starts floating due to bubbles of hydrogen gas sticking to its surface.
Inert metals like Au and Ag do not react with water.
Note: Try Balancing the above Chemical equations yourself
REACTION WITH ACIDS
Metal +dilute acid Salt + Hydrogen gas
metals react with dilute hydrochloric acid and dilute sulphuric acid to form chlorides.
Note : Copper, mercury and silver don’t react with dilute acids.
Hydrogen gas produced is oxidised to water. This happens because is a strong oxidising agent when metals react with nitric acid But Mg and Mn, react with very dilute nitric acid to evolve hydrogen gas. 4. Reaction of metals with other metal salts :
All metals are not equally reactive. Reactive metals can displace less reactive metals from their compounds in solution. This forms the basis of reactivity series of metals. Reactivity series is a list of metals arranged in order of their decreasing activities. 
REACTION OF NON-METALS :
| reaction with oxygen | non-metals form acidic oxides Eg:C+O2 ->CO2 |
| reaction with water | non-metals do not react with water because they cannot release electrons. |
| reaction with dilute acids | no reaction |
| reaction with salt solutions | a more reactive non-metal will displace less reactive non-metal from its salt solution. |
| reaction with chlorine | chloride is formed. Eg;H2(g)+Cl2->2HCl |
| reactions with hydrogen | hydrides are formed. H2 + S(l)->H2S |
Reaction between Metals and Non-Metals
- Reactivity of elements can be understood as a tendency to attain a completely filled valence shell.
- Atom of metals can lose electrons from valence shells to form cations(+ve ions).
- Atom of non-metals gain electrons in valence shell to form anions (–ve ions).
- Oppositely charged ions attract each other and are held by strong electrostatic forces of attraction forming ionic compounds.
Formation of
2,8, 22,8 (Magnesium ion) 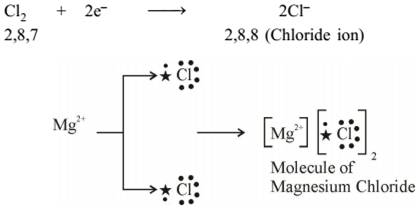
Properties of Ionic Compounds
- Are solid and mostly brittle.
- Have high melting and boiling points. More energy is required to break the strong inter-ionic attraction.
- Generally soluble in water and insoluble in kerosene, petrol.
- Conduct electricity in solution and in molten state. In both cases, free ions are formed and conduct electricity.
Occurrence of Metals Minerals : Elements or compounds occurring naturally are minerals. ORES : Mineral from which metal can be profitably extracted is an ore. For example, sulphide ore, oxide ore, carbonate ore.
- Metals at the bottom of activity series like gold, platinum, silver, copper generally occur in free state. But copper and silver also occur as sulphide and oxide ores.
- Metals of medium reactivity (Zn, Fe, Pb etc.) occur mainly as oxides,sulphides or carbonates.
- Metals of high reactivity (K, Na, Ca, Mg and Al) are very reactive and are thus found in combined state.
GANGUE : the commercially valueless materiallike soil,sand, etc. in which ore is found.called gangue. The gangue is removed from the ore. Various Methods to remove gangue: 1.GRAVITY SEPARATION 2.FROTH FLOATATION 3.MAGNETIC SEPARATION METALLURGY : Step-wise process of obtaining metal from its ore.
I. *Enrichment of ore
II. *Obtaining metal from enriched ore.
III. *Refining of impure metal to obtain pure metal.
Enrichment of Ores : It is the process of the removal of impurities such as soil, sand etc. from the ore prior to extraction of the metal. Different separation techniques are used based on physical or chemical properties of ore. Extracting Metals from the Enriched Ore
Extracting Metals Low in the Activity Series : By heating the ores in air at high temperature. e.g.*Mercury from cinnabar e.g. *Copper from copper sulphide Extracting Metals in the Middle of Activity Series : *Metals are easier to obtain from oxide ores, thus, sulphide and carbonate ores are converted into oxides. *Metal ore heated strongly in excess of air (Roasting) e.g..
Metal ore heated strongly in limited or no supply of air (Calcination) e.g..
Reduction of Metal Oxide :
USING COKE : Coke as a reducing agent.
USING DISPLACEMENT REACTION : highly reactive metal like Na, Ca and Al are used to displace metals of lower reactivity from their compounds. These displacement reactions are highly exothermic.
Thermite Reaction : Reduction of a metal oxide to form metal by using Al powder as a reducing agent. This process is used to join broken pieces of heavy iron objects or welding. Extracting Metals at the Top of Activity Series
- These metals have more affinity for oxygen than carbon so they cannot be obtained from their compounds by reducing with carbon.
- So are obtained by electrolytic reduction. e.g.Sodium is obtained by electrolysis of its molten chloride
As electricity is passed through the solution metal gets deposited at cathode and non-metal at anode. At cathode : e.g. At anode : III. Refining of Metals Impurities present in the obtained metal can be removed by electrolytic refining. Copper is obtained using this method. Following are present inside the electrolytic tank. Anode – slab of impure copper Cathode– slab of pure copper Solution – aqueous solution of copper sulphate with some dilute sulphuric acid From anode copper ions are released in the solution and equivalent amount of copper from solution is deposited at cathode. Insoluble impurities containing silver and gold gets deposited at the bottom of anode as anode mud. 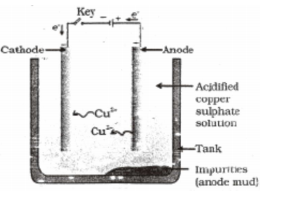
Corrosion Metals are attacked by substances in surroundings like moisture and acids. Silver – it reacts with sulphur in air to our form silver sulphide and articles become black. Copper – reacts with moist carbon dioxide in air and gains a green coat of copper carbonate. Iron-acquires a coating of a brown flaky substance called rust. Both air and moisture are necessary for rusting of iron. Rust is hydrated Iron (III) oxide i.e.
Prevention of Corrosion Rusting of iron is prevented by painting, oiling, greasing, galvanizing, chrome plating, anodising and making alloys.
In galvanization, iron or steel is coated with a layer of zinc because oxide thus formed is impervious to air and moisture thus protects further layers from corrosion.
Alloys: These are homogeneous mixture of metals with metals or non-metals. Adding small amount of carbon makes iron hard and strong.
Some examples of alloys are following ;
1. Steel : Hard Iron and carbon.Used for construction of roads, railways, other infrastructure, appliances
2. Stainless steel :Hard Rust Free Iron, nickel and chromium. Used in utensils.
3. Brass :Low electrical conductivity Copper and zinc.used for decoration for its bright gold-like appearance and in locks,gears ,plumbing and electrical appliances.
4. Bronze: than pure metal Copper and tin. used to make coins, springs, turbines and blades. 5. Solder : Low MP, used to weld wires Lead and tin. used to create a permanent bond between metal work pieces
6. Amalgam :Used by dentists. Mercury and any other metal
Metals and Non-metals class 10 Notes
- CBSE Revision notes (PDF Download) Free
- CBSE Revision notes for Class 10 Science PDF
- CBSE Revision notes Class 10 Science – CBSE
- CBSE Revisions notes and Key Points Class 10 Science
- Summary of the NCERT books all chapters in Science class 10
- Short notes for CBSE class 10th Science
- Key notes and chapter summary of Science class 10
- Quick revision notes for CBSE board exams
CBSE Class-10 Revision Notes and Key Points
Metals and Non-metals class 10 Notes. CBSE quick revision note for Class-10 Science, Chemistry, Maths, Biology and other subject are very helpful to revise the whole syllabus during exam days. The revision notes covers all important formulas and concepts given in the chapter. Even if you wish to have an overview of a chapter, quick revision notes are here to do if for you. These notes will certainly save your time during stressful exam days.
- Revision Notes for class-10 Mathematics
- Revision Notes for class-10 Science
- Revision Notes for class-10 Social Science
- Revision Notes for class-10 English Communicative
To download Metals and Non-metals class 10 Notes, sample paper for class 10 Mathematics, Social Science, Science, English Communicative; do check myCBSEguide app or website. myCBSEguide provides sample papers with solution, test papers for chapter-wise practice, NCERT solutions, NCERT Exemplar solutions, quick revision notes for ready reference, CBSE guess papers and CBSE important question papers. Sample Paper all are made available through the best app for CBSE students and myCBSEguide website.
- Chemical Reactions and Equations class 10 Notes Science
- Acids Bases and Salts class 10 Notes Science
- Metals and Non-metals class 10 Notes Science
- Carbon and its Compounds class 10 Notes Science
- Periodic Classification of Elements class 10 Notes Science
- Life Processes class 10 Notes Science
- Control and Coordination class 10 Notes Science
- How do Organisms Reproduce class 10 Notes Science
- Heredity and Evolution class 10 Notes Science
- Light Reflection and Refraction class 10 Notes Science
- Human Eye and Colourful World class 10 Notes Science
- Electricity class 10 Notes Science
- Magnetic Effects of Electric Current class 10 Notes Science
- Sources of Energy Current class 10 Notes Science
- Our Environment class 10 Notes Science
- Management of Natural Resources class 10 Notes Science

Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Create Now
myCBSEguide
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Install Now